- base_nameMaterial property base name
C++ Type:std::string
Controllable:No
Description:Material property base name
- blockThe list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied
C++ Type:std::vector<SubdomainName>
Controllable:No
Description:The list of blocks (ids or names) that this object will be applied
- boundaryThe list of boundaries (ids or names) from the mesh where this object applies
C++ Type:std::vector<BoundaryName>
Controllable:No
Description:The list of boundaries (ids or names) from the mesh where this object applies
- computeTrueWhen false, MOOSE will not call compute methods on this material. The user must call computeProperties() after retrieving the MaterialBase via MaterialBasePropertyInterface::getMaterialBase(). Non-computed MaterialBases are not sorted for dependencies.
Default:True
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:When false, MOOSE will not call compute methods on this material. The user must call computeProperties() after retrieving the MaterialBase via MaterialBasePropertyInterface::getMaterialBase(). Non-computed MaterialBases are not sorted for dependencies.
- constant_onNONEWhen ELEMENT, MOOSE will only call computeQpProperties() for the 0th quadrature point, and then copy that value to the other qps.When SUBDOMAIN, MOOSE will only call computeQpProperties() for the 0th quadrature point, and then copy that value to the other qps. Evaluations on element qps will be skipped
Default:NONE
C++ Type:MooseEnum
Controllable:No
Description:When ELEMENT, MOOSE will only call computeQpProperties() for the 0th quadrature point, and then copy that value to the other qps.When SUBDOMAIN, MOOSE will only call computeQpProperties() for the 0th quadrature point, and then copy that value to the other qps. Evaluations on element qps will be skipped
- declare_suffixAn optional suffix parameter that can be appended to any declared properties. The suffix will be prepended with a '_' character.
C++ Type:MaterialPropertyName
Controllable:No
Description:An optional suffix parameter that can be appended to any declared properties. The suffix will be prepended with a '_' character.
- elasticity_tensorelasticity_tensorThe name of the elasticity tensor.
Default:elasticity_tensor
C++ Type:MaterialPropertyName
Controllable:No
Description:The name of the elasticity tensor.
- large_kinematicsFalseUse a large displacement stress update.
Default:False
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:Use a large displacement stress update.
- prop_getter_suffixAn optional suffix parameter that can be appended to any attempt to retrieve/get material properties. The suffix will be prepended with a '_' character.
C++ Type:MaterialPropertyName
Controllable:No
Description:An optional suffix parameter that can be appended to any attempt to retrieve/get material properties. The suffix will be prepended with a '_' character.
ComputeStVenantKirchhoffStress
Stress update based on the first Piola-Kirchhoff stress
Overview
This class provides a hyperelastic St. Venant-Kirchhoff stress update defining the 2nd Piola-Kirchhoff stress as where is the Green-Lagrange strain and is an elasticity tensor calculated by a ComputeElasticityTensor object, with a name provided in the stress calculator input.
The model requires an isotropic elasticity tensor, as this is the only elasticity tensor that will lead to a truly hyperelastic model.
For small strains, when large_kinematics = false the model instead returns the standard linear elastic response, based on the elasticity tensor.
Figure 1 shows a typical material response under uniaxial stress. The plot shows the results in terms of the Cauchy stress and logarithmic strain to illustrate that the large deformation version of the model is in fact nonlinear.
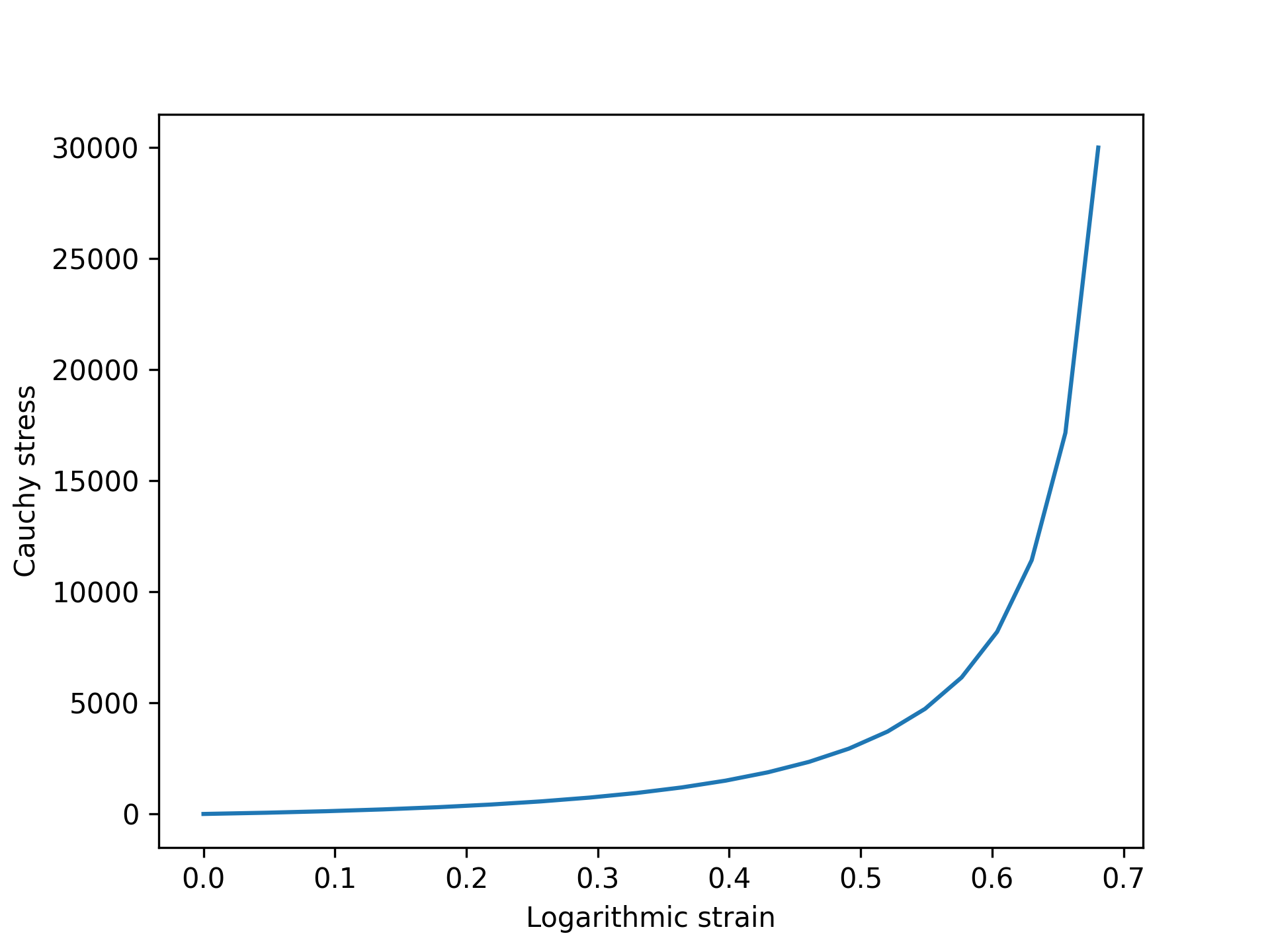
Figure 1: Response of the St. Venant-Kirchhoff model to uniaxial deformation, plotted as log strain versus Cauchy stress.
Example Input File Syntax
The follow example configures a large deformation St. Venant-Kirchhoff model using the default elasticity tensor name to define the response.
[Materials]
[elastic_tensor]
type = ComputeIsotropicElasticityTensor
shear_modulus = 67000.0
lambda = 40000.0
[]
[compute_stress]
type = ComputeStVenantKirchhoffStress
[]
[compute_strain]
type = ComputeLagrangianStrain
[]
[]
Input Parameters
- control_tagsAdds user-defined labels for accessing object parameters via control logic.
C++ Type:std::vector<std::string>
Controllable:No
Description:Adds user-defined labels for accessing object parameters via control logic.
- enableTrueSet the enabled status of the MooseObject.
Default:True
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:Yes
Description:Set the enabled status of the MooseObject.
- implicitTrueDetermines whether this object is calculated using an implicit or explicit form
Default:True
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:Determines whether this object is calculated using an implicit or explicit form
- seed0The seed for the master random number generator
Default:0
C++ Type:unsigned int
Controllable:No
Description:The seed for the master random number generator
- use_displaced_meshFalseWhether or not this object should use the displaced mesh for computation. Note that in the case this is true but no displacements are provided in the Mesh block the undisplaced mesh will still be used.
Default:False
C++ Type:bool
Controllable:No
Description:Whether or not this object should use the displaced mesh for computation. Note that in the case this is true but no displacements are provided in the Mesh block the undisplaced mesh will still be used.
Advanced Parameters
- output_propertiesList of material properties, from this material, to output (outputs must also be defined to an output type)
C++ Type:std::vector<std::string>
Controllable:No
Description:List of material properties, from this material, to output (outputs must also be defined to an output type)
- outputsnone Vector of output names where you would like to restrict the output of variables(s) associated with this object
Default:none
C++ Type:std::vector<OutputName>
Controllable:No
Description:Vector of output names where you would like to restrict the output of variables(s) associated with this object